Hey everyone, let’s dive into the fascinating world of Nickel-cadmium, or Ni-Cd, batteries! We’ll explore their history, how they work, their different designs, and finally, weigh their pros and cons.
First off, the history. Believe it or not, the development of Ni-Cd batteries wasn’t a single «eureka!» moment. It was a gradual process, with many scientists and inventors contributing over time. The very first rudimentary versions appeared in the late NINETEENTH century, with significant advancements happening throughout the TWENTIETH century. Early versions were bulky and inefficient, but persistent research led to the compact and reliable batteries we associate with the term today. Think about the early days of portable electronics – these batteries were instrumental in making things like early radios and power tools truly portable. The journey from those early, clunky prototypes to the sophisticated batteries we see now is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of better energy storage solutions.
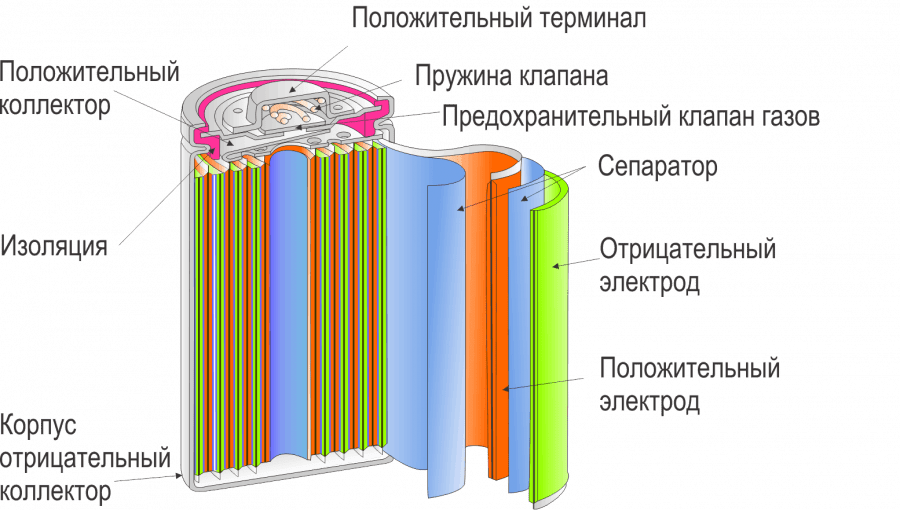
Now, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of how these batteries actually work. At the heart of a Ni-Cd battery is a simple yet elegant electrochemical process. It involves TWO electrodes – a nickel hydroxide electrode and a cadmium electrode – immersed in an alkaline electrolyte, usually potassium hydroxide. When the battery discharges, a chemical reaction occurs, releasing electrons that flow through an external circuit, powering your device. This flow of electrons is what we experience as electrical current. When you recharge the battery, the process reverses, essentially «pumping» the electrons back into the battery, restoring its chemical potential. It’s a cyclical process that can be repeated many times, making these batteries rechargeable. The specific chemical reactions are quite complex, involving oxidation and reduction processes at each electrode, but the core principle is this elegant exchange of electrons.
The design of the cadmium electrode is particularly interesting. There are TWO main types. One uses sintered cadmium powder, creating a porous structure that maximizes the surface area for the electrochemical reaction. This design is often favored for its high capacity and relatively long lifespan. The other type uses a different approach, employing a different structure for the cadmium electrode, often resulting in slightly different performance characteristics. These variations in design lead to subtle differences in the overall battery performance, such as energy density and discharge rate. Understanding these design differences helps explain why some Ni-Cd batteries might perform better in certain applications than others.
Let’s talk technical characteristics. Ni-Cd batteries are known for their relatively high energy density, meaning they can pack a lot of power into a small space. They also boast a long cycle life, meaning they can withstand many charge-discharge cycles before their capacity significantly degrades. Their discharge rate is generally quite good, meaning they can deliver a substantial amount of current quickly. However, their voltage is relatively constant throughout the discharge cycle, which is both an advantage and a disadvantage depending on the application. The nominal voltage of a single Ni-Cd cell is approximately ONE POINT TWO volts. You can combine multiple cells in series to achieve higher voltages.
Now, let’s discuss the advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, Ni-Cd batteries are known for their robustness and reliability. They can withstand a wide range of temperatures and are relatively tolerant to overcharging and discharging, making them quite forgiving. Their long cycle life is a significant advantage, especially in applications where frequent charging and discharging are necessary. They also have a relatively high discharge rate, making them suitable for applications requiring bursts of power.
However, there are downsides. One major drawback is the «memory effect.» This means that repeatedly charging the battery before it’s fully discharged can reduce its overall capacity over time. This is a significant limitation compared to more modern battery technologies. Another significant issue is the toxicity of cadmium. Cadmium is a heavy metal that is harmful to the environment and human health. This environmental concern has led to the phasing out of Ni-Cd batteries in many applications in favor of more environmentally friendly alternatives. The cost of Ni-Cd batteries is also generally higher compared to some other rechargeable battery types. These factors have significantly impacted their popularity in recent years.
Let’s dive into the world of Nickel-Cadmium, or Ni-Cd, batteries! First off, let’s talk about labeling. You’ll often see Ni-Cd batteries clearly labeled as such, sometimes with additional information like voltage and capacity (measured in milliampere-hours, or mAh). Look for the «Ni-Cd» designation – it’s the easiest way to identify them. Sometimes you might see other markings indicating the manufacturer or specific application. Always check the label before using a battery to ensure it’s appropriate for your device.
Now, a big question is how Ni-Cd batteries compare to other rechargeable options, specifically Lithium-ion and Nickel-Metal Hydride, or NiMH. Ni-Cd batteries are known for their robustness and ability to withstand a lot of charge-discharge cycles. They can handle being deeply discharged without significant damage, unlike some other battery chemistries. However, they have a lower energy density compared to Lithium-ion batteries, meaning they don’t pack as much power into the same size and weight. Compared to NiMH batteries, Ni-Cd batteries generally have a slightly longer lifespan in terms of charge-discharge cycles, but NiMH batteries often boast a higher energy density and are considered more environmentally friendly due to the absence of cadmium, a toxic heavy metal. The choice between these battery types really depends on the specific application and priorities.
Operating Ni-Cd batteries is relatively straightforward, but there are a few key rules to follow for optimal performance and longevity. Avoid completely discharging them; a partial discharge is better for their health. Also, avoid overcharging, as this can lead to reduced lifespan and even damage. Many chargers have built-in safeguards to prevent overcharging, but it’s always good practice to monitor the charging process. Regularly cycling the battery – fully charging and then fully discharging it – can help maintain its capacity, although this isn’t as crucial as with some other battery types. Finally, always use a charger specifically designed for Ni-Cd batteries; using the wrong charger can be dangerous.
What happens if your Ni-Cd battery loses its charge? Recovery is possible, but it depends on the extent of the discharge. If it’s just slightly depleted, a simple recharge should suffice. However, if it’s been deeply discharged and left for a long time, it might require a more involved process, sometimes involving a specialized charger or even a conditioning cycle. Deep discharges can lead to a phenomenon called the «memory effect,» where the battery seems to «remember» its lower capacity, but this effect is less pronounced in modern Ni-Cd batteries than it was in older ones. If your Ni-Cd battery seems to be losing its charge quickly or not holding a charge at all, it might be time to replace it.
Where do you actually find Ni-Cd batteries in use today? While Lithium-ion batteries have largely taken over many applications, Ni-Cd batteries still hold a place in certain niches. You might find them in older power tools, some emergency lighting systems, and certain industrial applications where their robustness and ability to withstand harsh conditions are valued. Their relatively low cost compared to some other battery types also contributes to their continued use in some sectors. However, their environmental impact due to the cadmium content is a growing concern, leading to a gradual phase-out in many areas.
Proper storage is essential for extending the lifespan of your Ni-Cd batteries. Store them in a cool, dry place, away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Avoid storing them fully charged or fully discharged; a partially charged state is generally ideal for long-term storage. Also, keep them away from conductive materials that could cause a short circuit. Following these simple storage guidelines can significantly extend the life of your Ni-Cd batteries.
Finally, let’s touch on some related news and developments. While Ni-Cd batteries are becoming less prevalent due to environmental concerns and the rise of alternative technologies, there’s ongoing research into improving their performance and addressing their limitations. There’s also ongoing discussion about responsible recycling and disposal of Ni-Cd batteries to minimize their environmental impact. Staying informed about these developments is crucial for making responsible choices regarding battery use and disposal.