So, what happens to your Lithium-ion batteries when the temperature plummets? It’s a common question, and the answer isn’t as simple as «they stop working.» Instead, the cold significantly impacts their performance. Think of it like this: the chemical reactions inside the battery that produce electricity slow down dramatically in freezing temperatures. This means you’ll get less power output, and the battery will drain faster than it would in warmer conditions. You might notice your phone dying quicker on a frigid day, or your electric vehicle having a reduced range. The cold also increases the internal resistance of the battery, making it harder for the electrons to flow freely and further reducing its efficiency. In extreme cases, prolonged exposure to very low temperatures can even cause permanent damage to the battery’s internal components, shortening its lifespan.
Now, can you store your Lithium-ion batteries in the cold? The short answer is: it’s not ideal, but it’s generally safer than leaving them in extreme heat. However, it’s crucial to understand that storing them in freezing conditions isn’t a long-term solution. While the cold slows down the chemical degradation processes that occur over time, it doesn’t stop them entirely. Ideally, you should store your Lithium-ion batteries in a cool, dry place, somewhere between FIFTEEN and TWENTY-FIVE degrees Celsius. If you absolutely must store them in the cold, try to keep them above ZERO degrees Celsius and ensure they are fully charged or at least at a FIFTY percent charge level. A completely depleted battery is more susceptible to damage in cold temperatures.
Charging Lithium-ion batteries in sub-zero temperatures is a big no-no. Doing so can severely damage the battery, potentially leading to a reduced lifespan or even complete failure. The chemical reactions involved in charging are already slowed by the cold, and forcing the process can cause uneven charging, leading to the formation of dendrites – tiny crystalline structures that can short-circuit the battery. This can be incredibly dangerous, potentially leading to overheating, fire, or even explosion. Always bring your battery inside to a warmer environment before attempting to charge it. Wait until it reaches a safe temperature, ideally above ZERO degrees Celsius, before plugging it in.
Keeping your Lithium-ion batteries working in freezing conditions requires a few simple rules. First, keep them warm. This doesn’t mean you need to keep them next to a heater, but carrying them in an inside pocket or using an insulated case can make a big difference. Second, avoid completely draining the battery. A partially charged battery will perform better in the cold than a completely depleted one. Third, limit the use of high-power applications. Things like using your phone’s camera extensively or running demanding apps will drain the battery faster in cold temperatures. Finally, remember that the battery will likely perform better if you let it warm up gradually before using it heavily.
The resistance to minus temperatures varies significantly depending on the type of Lithium-ion battery. Different chemistries, such as Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO), Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO), Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC), and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), all have different tolerances to cold. Generally, LFP batteries tend to perform better in low temperatures than LCO batteries. However, even the most cold-tolerant batteries will experience a performance decrease in freezing conditions. It’s crucial to consult the specifications of your specific battery to understand its limitations in cold weather.
Protecting your Lithium-ion storage devices from the cold is essential for extending their lifespan. Using insulated cases or bags is a simple and effective way to provide a buffer against the cold. Avoid leaving them exposed to the elements for extended periods. If you’re storing them in a cold environment, ensure the temperature remains above ZERO degrees Celsius. Regularly checking the battery’s charge level and avoiding complete depletion are also crucial preventative measures. Remember, a little preventative care can go a long way in ensuring your Lithium-ion batteries remain healthy and functional, even in the harshest winter conditions.
Hey everyone, let’s dive straight into how cold temperatures affect our trusty lithium-ion batteries. We recently conducted a test on several different lithium-ion batteries from various manufacturers and models – everything from those in your everyday phone to some higher-capacity power banks. The goal was to see exactly how these batteries perform under freezing conditions. We subjected them to a range of temperatures, from a comfortable room temperature down to well below freezing, and monitored their performance closely.
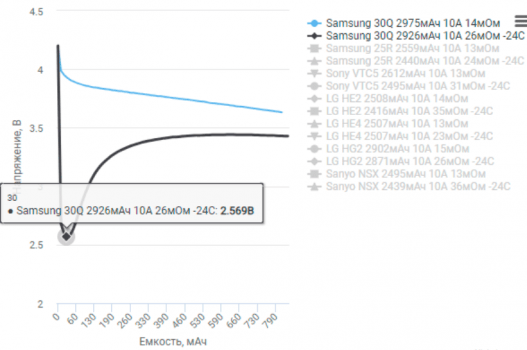
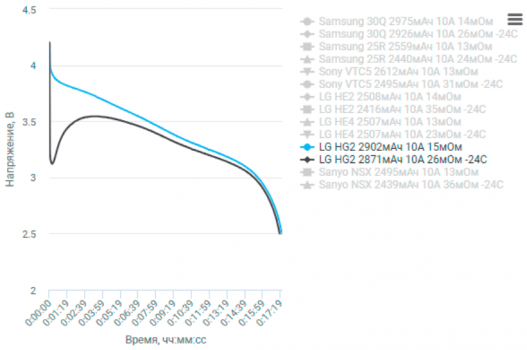
Now, the results were pretty interesting. We saw a significant variation in how different batteries handled the cold. Some performed surprisingly well, showing only a minor decrease in performance, while others… well, let’s just say they struggled. We meticulously documented the performance of each battery, noting things like charging time, discharge rate, and overall capacity. The differences were quite striking, highlighting the importance of choosing a battery designed for cold weather operation.
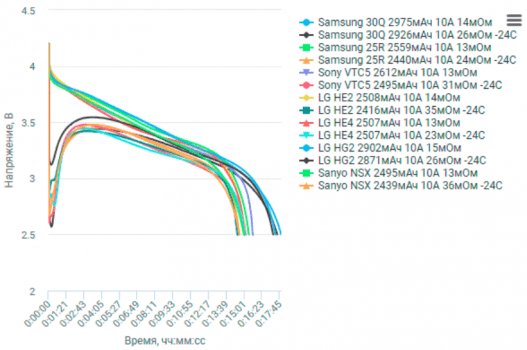
One of the most noticeable effects of the cold was the change in voltage. As the temperature dropped, we observed a consistent decrease in the output voltage of all the batteries tested. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing in itself, but it does mean that your devices might draw more current to compensate, potentially leading to faster battery drain. We recorded the voltage at various temperature points, and the data clearly showed a linear relationship – the colder it got, the lower the voltage went. This is something to keep in mind, especially if you rely on your devices in freezing conditions.
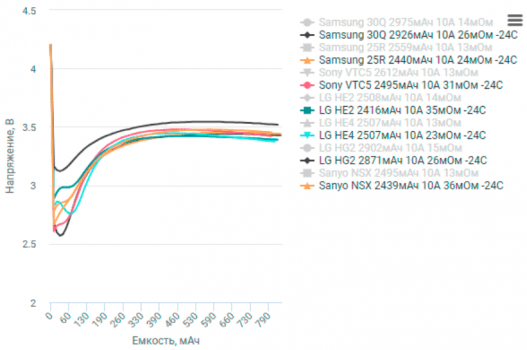
The impact on battery life was also significant. Across the board, we saw a reduction in the operational time of the batteries as the temperature decreased. This reduction wasn’t uniform, however. Some batteries experienced a relatively small decrease in runtime, while others saw their operational time cut almost in half. Again, the quality and design of the battery played a crucial role here. The data we collected clearly shows the importance of understanding how your specific battery will perform in the cold. We’ve included all the detailed graphs and charts in the description below, so you can see the exact performance figures for each battery we tested.
From our experiment, we can draw some key conclusions. Firstly, not all lithium-ion batteries are created equal when it comes to cold weather performance. Secondly, you should always expect a reduction in battery life and voltage output in freezing temperatures. And thirdly, choosing a battery specifically designed for cold weather operation can significantly improve your experience in such conditions. This is especially important for those who rely on their devices in cold climates or during winter activities.
Now, let’s talk about a specific example of a battery designed to withstand freezing temperatures: the Boston Power Swing FIVE THOUSAND THREE HUNDRED. This battery is known for its impressive cold-weather performance, and our tests confirmed its reputation. It showed significantly less performance degradation compared to other batteries we tested under the same conditions. This highlights the advancements being made in lithium-ion battery technology to address the challenges posed by cold temperatures.
Finally, we’ve included some links to relevant news articles and further research on lithium-ion batteries and cold weather performance in the description below. We encourage you to check them out for a more in-depth understanding of this topic. Remember, understanding how your batteries behave in different conditions is crucial for maximizing their lifespan and ensuring reliable performance.